When talking about diamonds, some people believe that the bigger the number, the better the stone. But diamonds (like other precious stones) are actually measured against the four C’s: Carat, Colour, Clarity and Cut. A large diamond could have a high carat weight, but low colour and clarity score, for example, which would seriously impact its value.
So if you’re thinking about buying a diamond or designing an engagement ring, read this simple guide to the four C’s then give our friendly team a call!
Carat
Carat is a unit of measurement. With gold, the carat value refers to its purity. With precious stones, it’s all about the weight. One carat is equal to 0.2g (or 0.007055oz in imperial measures).
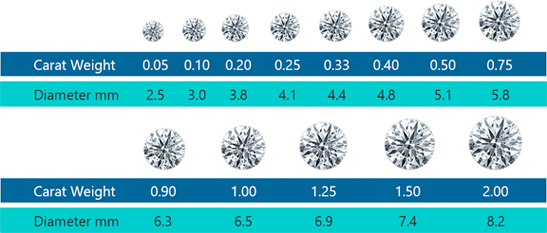
Note that the carat doesn’t indicate a diamond’s size. Some diamonds appear smaller than others with the same carat value (weight), because of the way they’ve been cut. There’s an optimal diameter/weight ratio you can use as a guide, as shown here.
Colour
There are many shades and grades of colour within each type of gemstone. Diamonds actually come in every colour of the rainbow, although most people are interested only in white diamonds. The best colour for a diamond is therefore no colour at all. A totally colourless diamond allows light to pass through it easily, resulting in the light being split into the full spectrum of the rainbow.
White diamonds are graded from totally colourless to light yellow, on a scale from D to Z. The differences between one grade and another are very subtle and it takes a trained eye and years of experience to colour grade a diamond.
Occasionally certain colours come into fashion. Pink diamonds on the likes of Blake Lively, Mariah Carey and Victoria Beckham and yellow (canary) diamonds seen on celebrities such as Jennifer Lopez, Heidi Klum and Kelly Clarkson have increased the popularity of these coloured stones, for example.
One other thing to be aware of when thinking about colour is fluorescence. Just over a quarter of all diamonds will visibly glow under UV light. This fluorescence will be rated on a diamond’s certificate as Nil, Faint, Medium, Strong or Very Strong. Fluorescence can be useful for diamonds rated K and below, as it can make them appear slightly whiter in daylight. For more colourless diamonds (D-J), strong fluorescence can have the opposite effect, making the diamonds appear milky and greatly reducing their value. That’s why it’s so important to talk to an expert when investing in diamonds (and that’s what we’re here for!).


Clarity
A gemstone’s clarity grade is directly related to its rarity – and the rarer the stone, the more value it has. Clarity refers to a gemstone’s relative freedom from ‘clarity characteristics’. Clarity characteristics can mean:
- inclusions, which lie within the stone
- blemishes, which lie on the surface of a gem
The fewer clarity characteristics, the more rare the gemstone.
However, each type of gemstone has its own clarity standards. For example, green tourmaline is naturally virtually inclusion-free, while emeralds almost always contain clarity characteristics. For this reason, transparent coloured gemstones are divided into clarity types. This allows each stone to be more fairly evaluated as it takes into account the individual nature of each gemstone. An emerald with an inclusion will always be more rare than a green tourmaline, so has far greater value, for example.
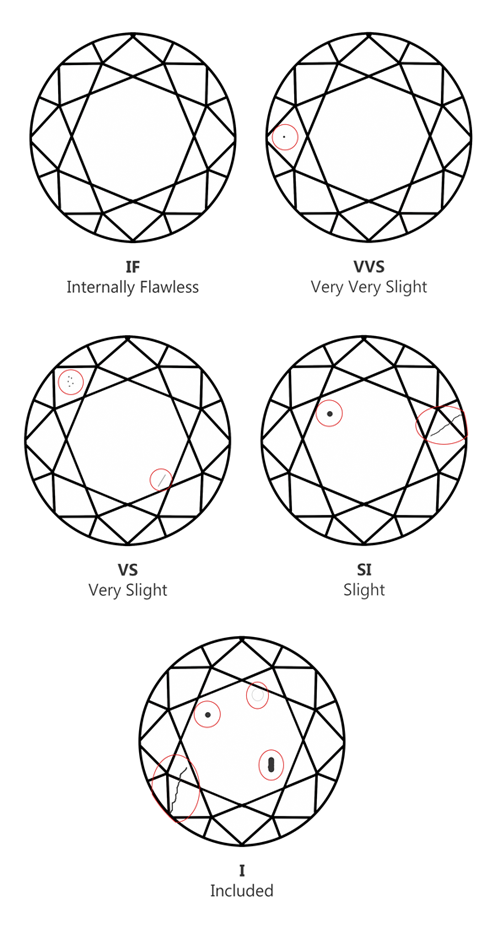
Diamonds have their own clarity types, as shown in this diagram. Talk to our team for more information about diamond clarity.
Cut
Cut refers to the shape or design of a stone, arrangement of facets, as well as the precision of the stone’s proportions and finish.
Proportions involve the balance and appeal of the basic design. Finish refers to the detail of the workmanship. A well-proportioned cut with a fine finish will show a stone’s optical properties to its fullest potential (think maximum sparkle!).
When the other three C’s are even, a better-cut gem will be more valuable. You can find the cut, polish and symmetry on any diamond certificate, each graded as either Excellent, Very Good, Good or Fair.
Diamonds can be carved or fashioned into almost any design imaginable, but we’ve listed some of the most popular cuts here.


What next?
If you feel ready to start experimenting with the four C’s and looking at the differences they can make to the cost of your ring, head to our diamonds website. You can play around with building your own ring, choosing the carat, colour, clarity and cut for yourself, which is a great way to put your new knowledge into practice and see how different choices impact the cost of a diamond ring.
If you’d like more help, that’s what we’re here for!
Our goldsmiths, led by Chris, and our resident gemologist Nicky have trained for years so that they can help you choose the right gemstones at the right prices. Get in touch to book an appointment or pop into one of our showrooms to say hello!


